成人哮喘患者中的炎症相关基因、外周血嗜酸性粒细胞(EOS)和嗜中性粒细胞(NEU)计数和肺功能
2015/11/16
摘要
研究背景:气道炎症作为哮喘的一个关键组成部分有赖于多种基因的相互作用。嗜酸性粒细胞及中性粒细胞能识别典型的炎症表型从而影响疾病的临床发展。
研究目标:同时评估成人哮喘15个炎症相关基因的单核苷酸多态性位点与嗜酸性粒细胞,中性粒细胞以及肺功能的相关性。
研究方法:在意大利的Verona,从呼吸系统疾病基因与环境的相互作用研究组(GEIRD 2008/2010)的实验对象中抽取年龄在20到64岁的337名哮喘患者,将其分成四个炎症组:低嗜酸性粒细胞(<3rd 四分位间距= 260 EOS/mm3)/低中性粒细胞组(<3rd quartile = 5,050 NEU/mm3), 低嗜酸性粒细胞/高中性粒细胞组, 高嗜酸性粒细胞/低中性粒细胞组, 高嗜酸性粒细胞/高中性粒细胞组。应用加性遗传模型(控制假发现率),单因素方法检测SNPs与炎症类型及使用支气管舒张剂前FEV%占预计值水平的相关性,从而筛选出SNPs,通过中介模式同时进行关联评估,其中把吸烟和过去三个月有使用哮喘控制药物作为潜在混杂因素。
研究结果:筛选出IL-18基因上的一个SNP位点做中介模式分析,中介模式描述如下图:
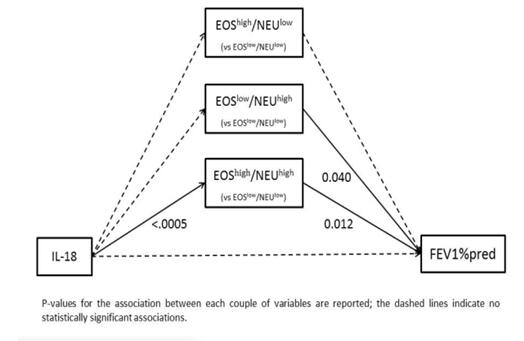
研究结论:本研究初步表明在IL-18基因的一个SNP位点与嗜酸性粒细胞高/中性粒细胞高组存在相关性,而其与肺功能无直接相关。
(南方医科大学南方医院 熊婧 赵海金 )
2015,ERS Meeting PA1234
Inflammation-related genes, peripheral blood eosinophil (EOS) and neutrophil (NEU) count, and lung function in adult asthma
Simone Accordini, Lucia Calciano, Cristina Bombieri, Giovanni Malerba, Francesca Belpinati, Marcello Ferrari, Anna Rita Lo Presti, Mario Olivieri, Elisabetta Zanolin, Roberto De Marco
2015,ERS Meeting PA1234
http://abstract.ersnet.org/my-abstract-book-2015/
Abstract
Background:Airway inflammation is a key component of asthma that depends on the interplay of multiple genes. Eosinophils and neutrophils have the ability to recognize distinct inflammatory phenotypes influencing the clinical characteristics of the disease.
Aim:To simultaneously assess the association among tag-SNPs located in 15 inflammation-related genes, EOS, NEU and lung function in adult asthma.
Methods:In Verona (Italy), 337 asthmatics (aged 20-64) were identified from the general population in the GEIRD study (2008/2010) and were classified into four inflammation groups: EOSlow (<3rd quartile = 260 EOS/mm3)/NEUlow (<3rd quartile = 5,050 NEU/mm3), EOSlow/NEUhigh, EOShigh/NEUlow, EOShigh/NEUhigh. SNPs were selected by testing their univariate association with the inflammation groups and pre-bronchodilator FEV1%pred under the additive genetic model (controlling the false discovery rate). The simultaneous relationships were evaluated by using a mediation model, with current smoking and the use of anti-asthmatic controller medications in the past three months as potential confounders
Results: A SNP in the IL-18 gene region was selected for the mediation analysis. The mediation model is described in this figure:
Conclusions:This preliminary analysis suggests that a SNP in the IL-18 gene region is associated with the EOShigh/NEUhigh pattern, without a direct association with lung function.
上一篇:
哮喘流行病学现状:系统评价
下一篇:
CompEx- 一个新的哮喘急性加重复合终点









